
- #WINDOWS 10 SLEEP VS HIBERNATE WINDOWS 10#
- #WINDOWS 10 SLEEP VS HIBERNATE PC#
- #WINDOWS 10 SLEEP VS HIBERNATE WINDOWS#
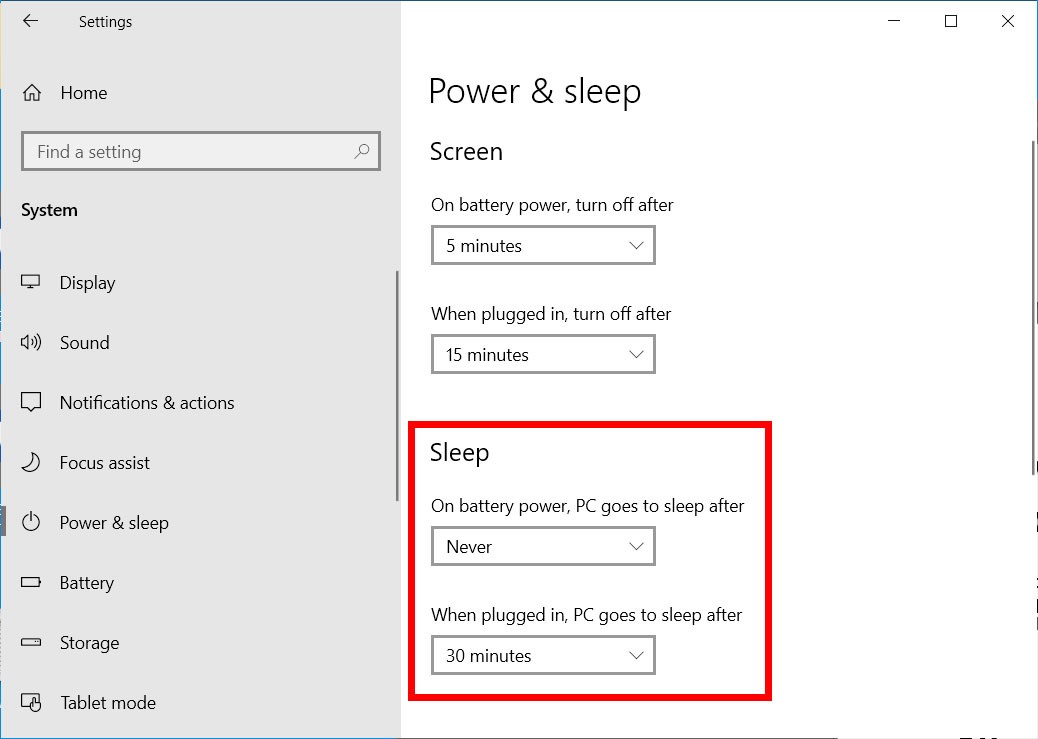
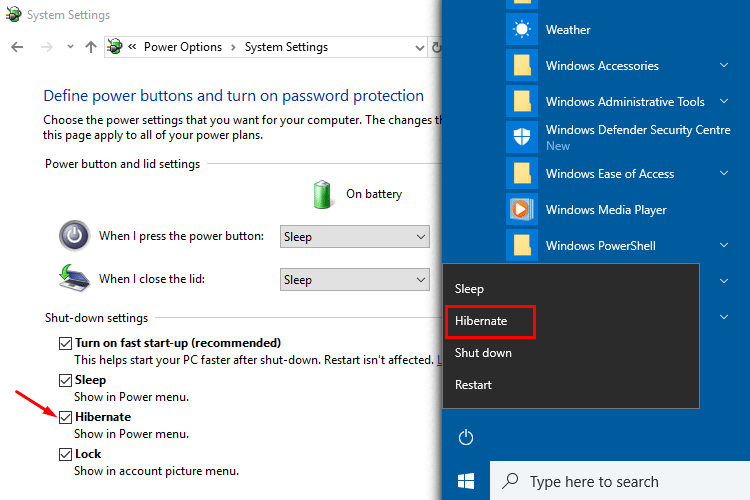
Select the right one for you between: “Do nothing”, “Sleep”, “Hibernate”, “Shut down”.Go to the section Power and sleep buttons and lid settings.You can change the power button and the shutdown settings as follow: Press the power button to get access to the session again.Ĭhanging your power buttons, lid and shutdown settings The next time you open the "Start menu" and select the "Power button", you will see that “Hibernate” is now available from the menu. In this case, you will see a banner saying “Some settings are managed by your system administrator”. Please note: If you are using a desktop or laptop managed by iSolutions, you might not be able to change these settings. Select Change settings that are currently unavailable.Choose the option What the power buttons do.
#WINDOWS 10 SLEEP VS HIBERNATE WINDOWS#
Windows provides several power-saving options for when you’re not using your device, helping to make it as efficient as possible. We explain what they are and when to use them.
#WINDOWS 10 SLEEP VS HIBERNATE PC#
When you turn on the PC again, you will be back to where you left off – even if this option is not as fast as the sleep mode. Technical differences: S3, the traditional standby model triggers the system to power down the CPU along with all power consuming components and peripherals while data are retained in the system memory (RAM). Click the magnifying glass icon in the bottom-left corner of your screen. When you are shutting down your PC, you can choose to:
#WINDOWS 10 SLEEP VS HIBERNATE WINDOWS 10#
Hibernate mode is also slightly safer, in that a power failure or running the battery completely down won't cause you to lose any work.This article guides you enabling “hibernate” mode on Windows 10 while turning the computer off. Then click on Change plan settings next to the power plan that’s enabled. When you turn the computer back on, all your apps and windows are restored just as if you had put it to sleep, but without the constant drain on the battery that sleep mode imposes. Right-click on the battery icon just as you’ve done above. All the same system settings are saved to a file on your computer's hard drive or SSD - which requires no power to maintain - and then the computer is shut down completely. If you're using a laptop, there's still a small drain on the battery to maintain RAM, but your entire desktop is restored almost instantly when you wake it up again. When you select it at shutdown, the current state of your computer (including all running apps, open windows, and temporary settings) is saved in RAM and your computer goes into a low-power mode. You may already be familiar with sleep mode.
With Hibernate Mode, you can: Use no power or battery life Resume. When you wake the computer up, the clocking starts, and it moves right on. Hibernating a PC gives you the best of both worlds when it comes to Sleep and shutting down. The memory is still powered, and everything else does nothing. Even so, hibernation is a useful feature, so you may want to enable it in Windows 11 and routinely use it to shut down your PC. Sleep mode in a nutshell stops the CPUs clocking, so the CPU stops right where it is. Modern, consumer-grade, Multi-Level Cell (MLC) NAND memory can generally endure about 3,000 to 5,000 P/E cycles before the storage’s integrity starts to deteriorate. Microsoft has been de-emphasizing the hibernation mode in Windows for years, perhaps to reduce confusion with the very similar sleep mode, which is available in the shutdown options.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
